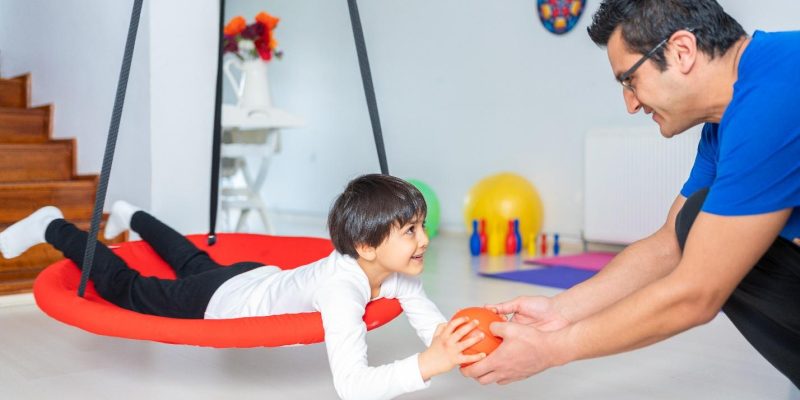
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurological condition characterized by difficulties with social interaction, communication, and repetitive or restricted behaviors. ASD affects each individual differently, leading to various levels of symptoms and severity that can significantly impair daily life.
On the other hand, occupational therapy (OT) is a holistic health discipline dedicated to helping individuals participate effectively in daily living activities. When applied to ASD patients, occupational therapists use strategies designed to increase abilities, increase independence, and ultimately boost the quality of life.
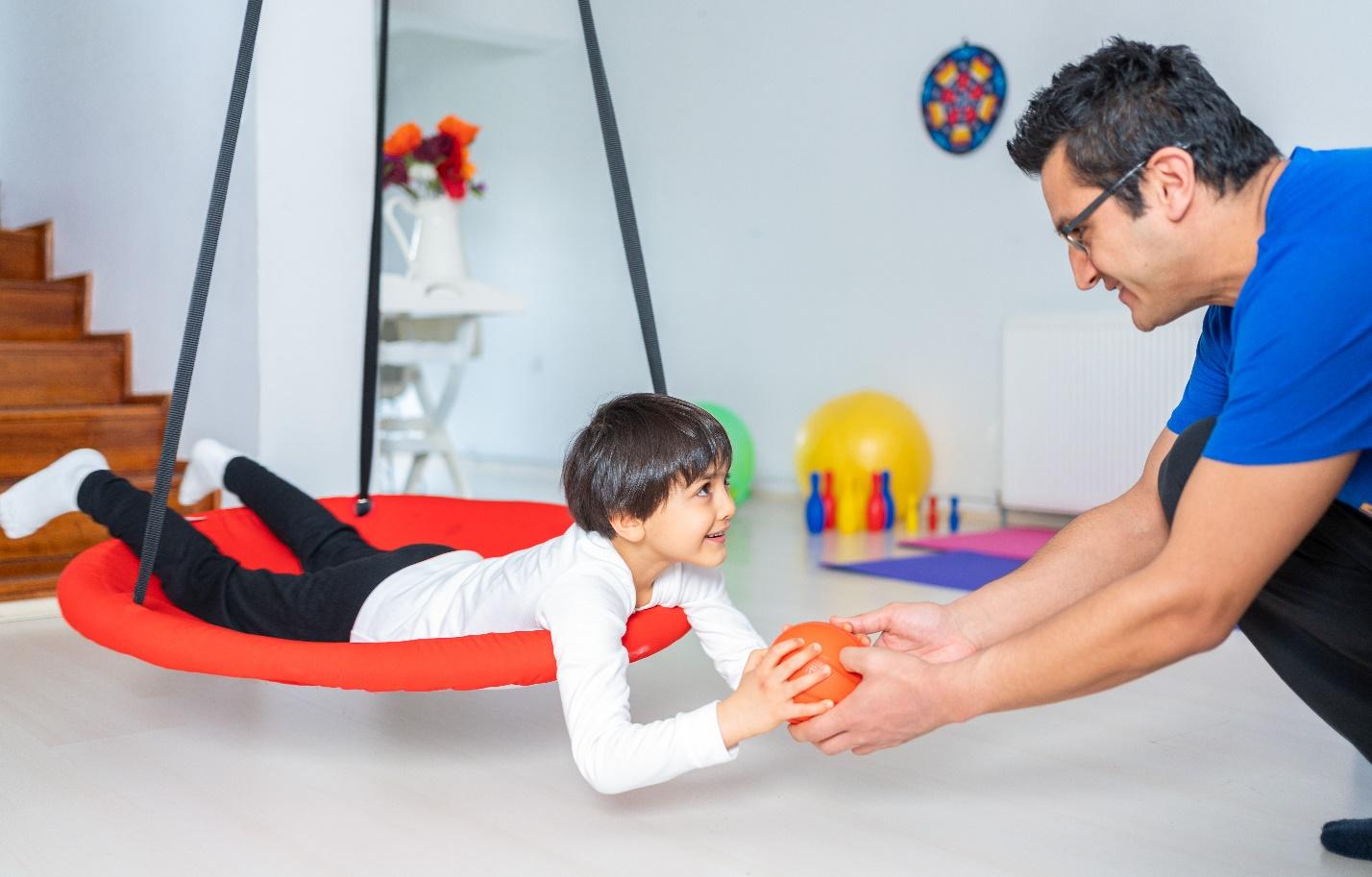

Occupational therapy assessment process for individuals with ASD
Occupational therapy is integral to helping individuals with ASD reach their maximum potential. An efficient assessment process is critical to understanding each person’s needs and creating interventions to optimize daily functioning.
The role of evaluation and assessment
Evaluation and assessment form the core of occupational therapy interventions for people living with ASD. Through this process, occupational therapists can gain comprehensive information about an individual’s strengths, challenges, and areas of difficulty and create targeted intervention plans tailored to each person’s unique needs that promote overall development and independence.
Also Read: Four Undeniable Benefits of Therapy that You Must Know
Understanding sensory processing in autism spectrum disorder
Sensory processing refers to how our brain receives and interprets sensory information from its environment. People with ASD often exhibit abnormal sensory processing patterns that negatively impact daily functioning. Occupational therapists conduct assessments to gain an understanding of an individual’s sensory processing difficulties as well as devise strategies to address them.
Tools and techniques used for assessment
- Sensory profile: The sensory profile is a standardized assessment tool to evaluate an individual’s sensory processing patterns. It provides invaluable information about their responses to various sensory stimuli (touch, movement, and sound stimuli), helping occupational therapists understand an individual’s preferences, sensitivities, and aversions more fully.
- Clinical observation: Through careful observation, occupational therapists can gain invaluable information about an individual’s motor skills, play abilities, social interactions, and self-care routines. Furthermore, statements provide insights into strengths, challenges, and areas for intervention that need addressing.
- Structured interviews: Occupational therapists often conduct structured interviews with those diagnosed with ASD and their caregivers to gather information regarding daily routines, functional abilities, and specific concerns. These interviews help therapists thoroughly understand an individual’s needs while providing an avenue for open communication between themselves and those they are helping.
- Standardized assessments: Standardized tests such as the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency (BOT-2) or Assessment of Motor and Process Skills (AMPS) provide objective measures of an individual’s motor skills, coordination, and daily activity performance, providing objective measures of an individual’s abilities that guide intervention planning.
- Functional assessments: Occupational therapists conduct practical assessments to assess an individual’s daily activities, such as dressing, eating, or school-related tasks. Functional assessments provide insight into specific challenges encountered by an individual and help occupational therapists create intervention strategies designed to increase independence and participation.
Occupational therapy assessment of individuals with ASD is essential to understanding their unique needs and tailoring interventions to promote overall development and independence. With tools and techniques like sensory profiles, clinical observation, structured interviews, standard assessments, and functional assessments, occupational therapists can gather all-inclusive data to tailor individualized intervention plans that help overcome challenges, enhance daily functioning, and reach the fullest potential for people with ASD.
Intervention strategies employed by occupational therapists
Occupational therapists play an invaluable role in helping individuals overcome difficulties and increase independence in daily activities. Their expert advice and intervention strategies effectively enable them to meet each client’s unique needs.
Development of daily living skills
American International College offers occupational therapy doctorate programs to equip students with strategies to develop and strengthen an individual’s conversational skills. Students learn to develop essential life skills through mastering intervention techniques, including dressing, cooking, and managing chores. They’re specially trained to collaborate closely with clients, identifying their challenges and creating tailored interventions to achieve optimal progress. Such programs instill the skills to break tasks into manageable parts using adaptive strategies, helping individuals, including those living with mental health conditions, reenter the workforce while maintaining independence.
Sensory integration therapies
Sensory integration therapies are an integral component of occupational therapy interventions. Many individuals struggle with sensory processing challenges that prevent them from integrating and responding appropriately to sensory stimuli, so occupational therapists employ sensory integration techniques to help individuals regulate their responses and engage in meaningful activities more efficiently. Such therapies may include sensory diets, special equipment, or structured sensory experiences that optimize sensory processing and promote optimal functioning.
Enhance social and communication skills
Occupational therapists recognize the significance of social and communication skills for cultivating meaningful relationships and successful participation across various contexts. They employ intervention strategies to strengthen these abilities in individuals with autism spectrum disorder, developmental delays, or social anxiety issues. Therapists facilitate social interactions while teaching effective communication strategies; opportunities are also provided for practice in real-life scenarios. By emphasizing nonverbal cues, active listening techniques, and social problem-solving, occupational therapists help individuals gain the necessary tools for successfully navigating social interactions.
Use of assistive technology in intervention
Assistive technology plays an integral part in occupational therapy interventions today. Occupational therapists leverage technological advancements to expand clients’ functional abilities and promote independence; assistive devices such as adaptive switches, speech-to-text software, and mobility aids enable individuals to overcome physical and cognitive challenges. Therapists assess clients’ needs before providing personalized solutions using assistive technologies that support daily activities, communication, and mobility, empowering people to overcome barriers and reach greater autonomy.
Due to the wide-ranging symptoms associated with ASD, strategies that work for one individual may not necessarily work for another. Therefore, occupational therapists continually adapt their methods and techniques to meet individual needs, learning from each challenge they encounter while innovating their practice to better assist those living with ASD.
Also Read: Shockwave Therapy for ED – Things You Should Know About
Conclusion
Occupational therapy plays an essential role in helping those living with ASD. OTs enable these individuals to navigate life more freely and confidently by emphasizing critical skills and taking an individualized approach.
Even with significant advances in this area, much remains to be explored. Future research must strive to gain a deeper understanding of ASD while further refining therapeutic strategies—not simply managing symptoms but optimizing potential. Innovation is the way forward regarding personalized therapy; therefore, the future seems bright for ASD occupational therapy.